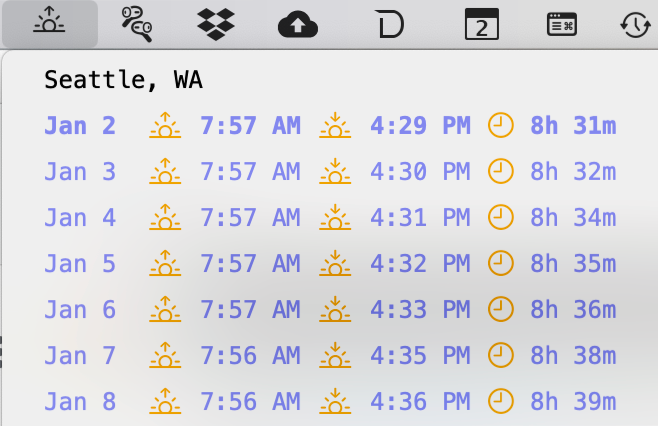
Displays sunrise, sunset, and day length for a location.
#!/usr/bin/env xcrun swift
/*
* <xbar.title>Sunrise</xbar.title>
* <xbar.version>v1.1.1</xbar.version>
* <xbar.author>Brad Greenlee</xbar.author>
* <xbar.author.github>bgreenlee</xbar.author.github>
* <xbar.desc>Displays sunrise, sunset, and day length for a location.</xbar.desc>
* <xbar.image>https://raw.githubusercontent.com/bgreenlee/SunriseBitBar/main/sunrise-bitbar.png</xbar.image>
* <xbar.dependencies>Xcode,swift</xbar.dependencies>
* <xbar.abouturl>https://github.com/bgreenlee/SunriseBitBar</xbar.abouturl>
*/
// Customizations
let LOCATION = "Seattle, WA" // or lat,lon coordinates
let DAYS = 7 // number of days to show
let PAST_DAYS = 0 // number of days in the past to show
let TIME_STYLE:DateFormatter.Style = .short // .short, .medium, .long, .full
let LOCATION_FONT = "Menlo"
let LOCATION_COLOR = "black"
let SUNRISE_FONT = "Menlo"
let SUNRISE_COLOR = "blue"
let SYMBOL_COLOR = "orange"
// Main code
let coordinate = try parseLocation(LOCATION)
// Reverse geocode so we can get the timezone in the location
let coder = CLGeocoder()
let loc = CLLocation(latitude: coordinate.latitude, longitude: coordinate.longitude)
var placemark: CLPlacemark?
var timezone: TimeZone?
coder.reverseGeocodeLocation(loc) { (placemarks, error) in
placemark = placemarks?.last
timezone = placemark?.timeZone
CFRunLoopStop(CFRunLoopGetCurrent())
}
CFRunLoopRun() // wait for reverse geocode to finish
print(":sunrise:\n---\n")
if let placemark = placemark {
if let city = placemark.locality, let administrativeArea = placemark.administrativeArea, let country = placemark.country {
if country == "United States" {
print("\(city), \(administrativeArea)|font=\(LOCATION_FONT) color=\(LOCATION_COLOR)")
} else {
print("\(city), \(administrativeArea), \(country)|font=\(LOCATION_FONT) color=\(LOCATION_COLOR)")
}
} else {
print("\(placemark.name ?? "Unknown")")
}
}
let today = Date()
for i in -PAST_DAYS..<DAYS-PAST_DAYS {
let date = Calendar.current.date(byAdding: .day, value: i, to: today)!
if let (sunrise, sunset) = NTSolar.sunRiseAndSet(forDate: date, atLocation: coordinate, inTimeZone: timezone!) {
let dateFormatter = DateFormatter()
dateFormatter.setLocalizedDateFormatFromTemplate("MMMd")
print(dateFormatter.string(from: date).padding(toLength: 7, withPad: " ", startingAt: 0), terminator:"")
let timeFormatter = DateFormatter()
timeFormatter.dateStyle = .none
timeFormatter.timeStyle = TIME_STYLE
if let timezone = timezone {
timeFormatter.timeZone = timezone
}
let sunriseTime = timeFormatter.string(from: sunrise).lowercased()
let sunsetTime = timeFormatter.string(from: sunset).lowercased()
let daylengthFormatter = DateComponentsFormatter()
daylengthFormatter.unitsStyle = .abbreviated
daylengthFormatter.allowedUnits = [.minute, .hour]
let formattedDayLength = daylengthFormatter.string(from: sunrise, to: sunset)!
print(":sunrise: \(sunriseTime) :sunset: \(sunsetTime) :clock: \(formattedDayLength)|font=\(SUNRISE_FONT)\(i == 0 ? "-Bold" : "") color=\(SUNRISE_COLOR) sfcolor=\(SYMBOL_COLOR)")
}
}
struct ValidationError: Error, CustomStringConvertible {
var description:String
init(_ description:String) {
self.description = description
}
}
func parseLocation(_ argument: String) throws -> CLLocationCoordinate2D {
let parts = argument.components(separatedBy: ",")
if parts.count == 2, let latitude = Double(parts[0]), let longitude = Double(parts[1]) {
return CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: latitude, longitude: longitude)
} else {
// see if we can geocode it
let coder = CLGeocoder()
var location: CLLocation?
coder.geocodeAddressString(argument) { (placemarks, error) in
location = placemarks?.last?.location
CFRunLoopStop(CFRunLoopGetCurrent())
}
CFRunLoopRun()
if let location = location {
return location.coordinate
}
throw ValidationError("Could not parse location. Provide either a valid place name or latitude,longitude.")
}
}
//
//
// NTSolar.swift
//
// Created by Neil Tiffin on 5/8/19.
// Copyright © 2019 Performance Champions, Inc.
// Copyright © 2019 Neil Tiffin.
//
// Released to the public domain by Neil Tiffin, May 2019
// Released to the public domain by Performance Champions, Inc., May 2019
//
import Foundation
import CoreLocation
var stderr = FileHandle.standardError
extension FileHandle : TextOutputStream {
public func write(_ string: String) {
guard let data = string.data(using: .utf8) else { return }
self.write(data)
}
}
/// Class to calculate sunrise sunset.
///
/// C code originally from: [http://stjarnhimlen.se/comp/sunriset.c](http://stjarnhimlen.se/comp/sunriset.c)
class NTSolar {
// MARK: - Public Swift Interface
/// Calculate the sun rise and set times.
///
/// - Parameters:
/// - forDate: The date for the calculation. You should ensure that the date, which is stored as UTC, is the date
/// really wanted in the given time zone. It will be converted to the given time zone before being used.
/// - atLocation: The latitude and longitude for the calculation.
/// - inTimeZone: The time zone for the resulting date and times.
/// - Returns: If the sun both rises and sets on the day requested and at the
/// latitude requested then return sun rise and set times rounded down to the minute, nil othewise.
class func sunRiseAndSet(forDate: Date,
atLocation: CLLocationCoordinate2D,
inTimeZone: TimeZone) -> (sunrise: Date, sunset: Date)? {
var calendar = Calendar(identifier: .gregorian)
calendar.timeZone = inTimeZone
var comp = calendar.dateComponents([.day, .year, .month], from: forDate)
comp.calendar = calendar
guard let year = comp.year,
let month = comp.month,
let day = comp.day else {
print("Failed to find date components.", to:&stderr)
return nil
}
let (riseUTC, setUTC, code) = NTSolar.sun_rise_set(year: year,
month: month,
day: day,
lon: atLocation.longitude,
lat: atLocation.latitude)
if code != .RiseAndSet {
print("Failed to find rise and set.", to:&stderr)
return nil
}
// Calc sunrise
var riseLocalHrs = riseUTC + (Double(inTimeZone.secondsFromGMT()) / 3600.0)
if riseLocalHrs > 24.0 {
riseLocalHrs -= 24.0
}
let riseHoursInt = Int(riseLocalHrs)
comp.hour = riseHoursInt
comp.minute = Int( (( riseLocalHrs - Double(riseHoursInt) ) * 60.0).rounded() )
comp.second = 0
comp.nanosecond = 0
guard let riseTime = comp.date else {
print("\nFailed to calculate rise time hrs: \(riseLocalHrs).\n\(comp)\n", to:&stderr)
return nil
}
// Calc sunset
var setLocalHrs = setUTC + (Double(inTimeZone.secondsFromGMT()) / 3600.0)
if setLocalHrs > 24.0 {
setLocalHrs -= 24.0
}
let setHoursInt = Int(setLocalHrs)
comp.hour = setHoursInt
comp.minute = Int( ((setLocalHrs - Double(setHoursInt) ) * 60.0).rounded() )
comp.second = 0
comp.nanosecond = 0
guard let setTime = comp.date else {
print("\nFailed to calculate set time hrs: \(setLocalHrs).\n\(comp)\n", to:&stderr)
return nil
}
return (riseTime, setTime)
}
// MARK: - SUNRISET.C
// C code originally from: [http://stjarnhimlen.se/comp/sunriset.c](http://stjarnhimlen.se/comp/sunriset.c)
//
// The conversion process removed pointers in favor of return tuples, converted macros to function calls,
// added return code enum, and converted
// comments to work with Xcode. Of course the C code had to be converted to Swift, but that was minimal.
//
// As much as possible the original code was left intact in order to not introduce bugs.
// In other words, some code was left unfashionable by today's standards.
enum ReturnCode: Int {
/// Sun is below the specified "horizon" 24 hours
/// "Day" length = 0 hours, trise and tset are
/// both set to the time when the sun is at south.
case SunAlwaysBelow = -1
/// Sun rises/sets this day, times stored at rise and set.
case RiseAndSet = 0
/// Sun above the specified "horizon" 24 hours.
/// trise set to time when the sun is at south,
/// minus 12 hours while tset is set to the south
/// time plus 12 hours. "Day" length = 24 hours
case SunAlwaysAbove = 1
}
/* +++Date last modified: 05-Jul-1997 */
/* Updated comments, 05-Aug-2013 */
/*
SUNRISET.C - computes Sun rise/set times, start/end of twilight, and
the length of the day at any date and latitude
Written as DAYLEN.C, 1989-08-16
Modified to SUNRISET.C, 1992-12-01
(c) Paul Schlyter, 1989, 1992
Released to the public domain by Paul Schlyter, December 1992
*/
/// A macro to compute the number of days elapsed since 2000 Jan 0.0
/// (which is equal to 1999 Dec 31, 0h UT)
private class func days_since_2000_Jan_0(y:Int, m:Int, d:Int) -> Int {
return (367*(y)-((7*((y)+(((m)+9)/12)))/4)+((275*(m))/9)+(d)-730530)
}
/* Some conversion factors between radians and degrees */
private static let PI = 3.1415926535897932384
private static let RADEG = ( 180.0 / PI )
private static let DEGRAD = ( PI / 180.0 )
/* The trigonometric functions in degrees */
private class func sind(x: Double) -> Double { return sin((x)*DEGRAD) }
private class func cosd(x: Double) -> Double { return cos((x)*DEGRAD) }
private class func tand(x: Double) -> Double { return tan((x)*DEGRAD) }
private class func atand(x: Double) -> Double { return (RADEG*atan(x)) }
private class func asind(x: Double) -> Double { return (RADEG*asin(x)) }
private class func acosd(x: Double) -> Double { return (RADEG*acos(x)) }
private class func atan2d(y: Double,x: Double)-> Double { return (RADEG*atan2(y,x)) }
/* Following are some macros around the "workhorse" function __daylen__ */
/* They mainly fill in the desired values for the reference altitude */
/* below the horizon, and also selects whether this altitude should */
/* refer to the Sun's center or its upper limb. */
/** This macro computes the length of the day, from sunrise to sunset. */
/** Sunrise/set is considered to occur when the Sun's upper limb is */
/** 35 arc minutes below the horizon (this accounts for the refraction */
/** of the Earth's atmosphere). */
class func day_length(year: Int, month: Int, day: Int, lon: Double, lat: Double) -> Double {
return daylen( year: year, month: month, day: day, lon: lon, lat: lat, altit: -35.0/60.0, upper_limb: 1 )
}
/** This macro computes the length of the day, including civil twilight. */
/** Civil twilight starts/ends when the Sun's center is 6 degrees below */
/** the horizon. */
class func day_civil_twilight_length(year: Int, month: Int, day: Int, lon: Double, lat: Double) -> Double {
return daylen( year: year, month: month, day: day, lon: lon, lat: lat, altit: -6.0, upper_limb: 0 )
}
/** This macro computes the length of the day, incl. nautical twilight. */
/** Nautical twilight starts/ends when the Sun's center is 12 degrees */
/** below the horizon. */
class func day_nautical_twilight_length(year: Int, month: Int, day: Int, lon: Double, lat: Double) -> Double {
return daylen( year: year, month: month, day: day, lon: lon, lat: lat, altit: -12.0, upper_limb: 0 )
}
/** This macro computes the length of the day, incl. astronomical twilight. */
/** Astronomical twilight starts/ends when the Sun's center is 18 degrees */
/** below the horizon. */
class func day_astronomical_twilight_length(year: Int, month: Int, day: Int, lon: Double, lat: Double) -> Double {
return daylen( year: year, month: month, day: day, lon: lon, lat: lat, altit: -18.0, upper_limb: 0 )
}
/** This macro computes times for sunrise/sunset. */
/** Sunrise/set is considered to occur when the Sun's upper limb is */
/** 35 arc minutes below the horizon (this accounts for the refraction */
/** of the Earth's atmosphere). */
class func sun_rise_set(year: Int, month: Int, day: Int , lon: Double, lat: Double) -> (trise: Double, tset: Double, code: ReturnCode) {
let (start, end, code) = sunriset( year: year, month: month, day: day, lon: lon, lat: lat, altit: -35.0/60.0, upper_limb: 1)
return (start, end, code)
}
/** This macro computes the start and end times of civil twilight. */
/** Civil twilight starts/ends when the Sun's center is 6 degrees below */
/** the horizon. */
class func civil_twilight(year: Int, month: Int, day: Int, lon: Double, lat: Double) -> (trise: Double, tset: Double, code: ReturnCode) {
let (start, end, code) = sunriset( year: year, month: month, day: day, lon: lon, lat: lat, altit: -6.0, upper_limb: 0)
return (start, end, code)
}
/** This macro computes the start and end times of nautical twilight. */
/** Nautical twilight starts/ends when the Sun's center is 12 degrees */
/** below the horizon. */
class func nautical_twilight(year: Int, month: Int ,day: Int, lon: Double, lat: Double) -> (trise: Double, tset: Double, code: ReturnCode) {
let (start, end, code) = sunriset( year: year, month: month, day: day, lon: lon, lat: lat, altit: -12.0, upper_limb: 0)
return (start, end, code)
}
/** This macro computes the start and end times of astronomical twilight. */
/** Astronomical twilight starts/ends when the Sun's center is 18 degrees */
/** below the horizon. */
class func astronomical_twilight(year: Int, month: Int, day: Int, lon: Double, lat: Double) -> (trise: Double, tset: Double, code: ReturnCode) {
let (start, end, code) = sunriset( year: year, month: month, day: day, lon: lon, lat: lat, altit: -18.0, upper_limb: 0)
return (start, end, code)
}
/// The "workhorse" function for sun rise/set times
///
/// - Parameters:
/// - year: calendar date, 1801-2099 only.
/// - month: calendar date, 1801-2099 only.
/// - day: calendar date, 1801-2099 only.
/// - lon: Eastern longitude positive, Western longitude negative. The longitude value IS critical in this function!
/// - lat: Northern latitude positive, Southern latitude negative
/// - altit: the altitude which the Sun should cross. Set to -35/60 degrees for rise/set, -6 degrees
/// for civil, -12 degrees for nautical and -18 degrees for astronomical twilight.
/// - upper_limb: non-zero -> upper limb, zero -> center
/// Set to non-zero (e.g. 1) when computing rise/set
/// times, and to zero when computing start/end of twilight.
/// - Returns: rise, set, code.
///
/// Both times in hours UT are relative to the specified altitude,
/// and thus this function can be used to compute
/// various twilight times, as well as rise/set times.
///
/// Code 0 = sun rises/sets this day, times stored at rise and set.
///
/// Code +1 = sun above the specified "horizon" 24 hours.
/// *trise set to time when the sun is at south,
/// minus 12 hours while *tset is set to the south
/// time plus 12 hours. "Day" length = 24 hours
///
/// Code -1 = sun is below the specified "horizon" 24 hours
/// "Day" length = 0 hours, *trise and *tset are
/// both set to the time when the sun is at south.
private class func sunriset(year: Int,
month: Int,
day: Int,
lon: Double,
lat: Double,
altit: Double,
upper_limb: Int) -> (trise: Double, tset: Double, code: ReturnCode) {
var altit = altit
var d: Double /* Days since 2000 Jan 0.0 (negative before) */
var sr: Double /* Solar distance, astronomical units */
var sRA: Double /* Sun's Right Ascension */
var sdec: Double /* Sun's declination */
var sradius: Double /* Sun's apparent radius */
var t: Double /* Diurnal arc */
var tsouth: Double /* Time when Sun is at south */
var sidtime: Double /* Local sidereal time */
var rc: ReturnCode = ReturnCode.RiseAndSet /* Return cde from function - usually 0 */
/* Compute d of 12h local mean solar time */
d = Double(days_since_2000_Jan_0(y: year,m: month,d: day)) + 0.5 - lon/360.0;
/* Compute the local sidereal time of this moment */
sidtime = revolution( x: GMST0(d: d) + 180.0 + lon )
/* Compute Sun's RA, Decl and distance at this moment */
(sRA, sdec, sr) = sun_RA_dec(d: d)
/* Compute time when Sun is at south - in hours UT */
tsouth = 12.0 - rev180(x: sidtime - sRA)/15.0
/* Compute the Sun's apparent radius in degrees */
sradius = 0.2666 / sr
/* Do correction to upper limb, if necessary */
if upper_limb != 0 {
altit -= sradius
}
/* Compute the diurnal arc that the Sun traverses to reach */
/* the specified altitude altit: */
do {
let cost: Double = ( sind(x: altit) - sind(x: lat) * sind(x: sdec) ) / ( cosd(x: lat) * cosd(x: sdec) );
if ( cost >= 1.0 ) {
rc = ReturnCode.SunAlwaysBelow
t = 0.0 /* Sun always below altit */
}
else if ( cost <= -1.0 ) {
rc = ReturnCode.SunAlwaysAbove
t = 12.0 /* Sun always above altit */
}
else {
t = acosd(x: cost)/15.0 /* The diurnal arc, hours */
}
}
/* Store rise and set times - in hours UT */
let trise = tsouth - t;
let tset = tsouth + t;
return (trise, tset, rc)
} /* __sunriset__ */
/// The "workhorse" function
///
/// - Parameters:
/// - year: year,month,date = calendar date, 1801-2099 only.
/// - month: year,month,date = calendar date, 1801-2099 only.
/// - day: year,month,date = calendar date, 1801-2099 only.
/// - lon: Eastern longitude positive, Western longitude negative
/// - lat: Northern latitude positive, Southern latitude negative
/// - altit: altit = the altitude which the Sun should cross
/// Set to -35/60 degrees for rise/set, -6 degrees
/// for civil, -12 degrees for nautical and -18
/// degrees for astronomical twilight.
/// - upper_limb: upper_limb: non-zero -> upper limb, zero -> center
/// Set to non-zero (e.g. 1) when computing day length
/// and to zero when computing day+twilight length.
/// - Returns: Day number
private class func daylen(year: Int, month: Int, day: Int, lon: Double, lat: Double,
altit: Double, upper_limb: Int ) -> Double {
/**********************************************************************/
/* Note: year,month,date = calendar date, 1801-2099 only. */
/* Eastern longitude positive, Western longitude negative */
/* Northern latitude positive, Southern latitude negative */
/* The longitude value is not critical. Set it to the correct */
/* longitude if you're picky, otherwise set to to, say, 0.0 */
/* The latitude however IS critical - be sure to get it correct */
/* altit = the altitude which the Sun should cross */
/* Set to -35/60 degrees for rise/set, -6 degrees */
/* for civil, -12 degrees for nautical and -18 */
/* degrees for astronomical twilight. */
/* upper_limb: non-zero -> upper limb, zero -> center */
/* Set to non-zero (e.g. 1) when computing day length */
/* and to zero when computing day+twilight length. */
/**********************************************************************/
var altit = altit
var d: Double /* Days since 2000 Jan 0.0 (negative before) */
var obl_ecl: Double /* Obliquity (inclination) of Earth's axis */
var sr: Double /* Solar distance, astronomical units */
var slon: Double /* True solar longitude */
var sin_sdecl: Double /* Sine of Sun's declination */
var cos_sdecl: Double /* Cosine of Sun's declination */
var sradius: Double /* Sun's apparent radius */
var t: Double /* Diurnal arc */
/* Compute d of 12h local mean solar time */
d = Double(days_since_2000_Jan_0(y: year, m: month, d: day)) + 0.5 - lon/360.0;
/* Compute obliquity of ecliptic (inclination of Earth's axis) */
obl_ecl = 23.4393 - 3.563E-7 * d;
/* Compute Sun's ecliptic longitude and distance */
(slon, sr) = sunpos( d: d )
/* Compute sine and cosine of Sun's declination */
sin_sdecl = sind(x: obl_ecl) * sind(x: slon);
cos_sdecl = sqrt( 1.0 - sin_sdecl * sin_sdecl );
/* Compute the Sun's apparent radius, degrees */
sradius = 0.2666 / sr;
/* Do correction to upper limb, if necessary */
if upper_limb != 0 {
altit -= sradius
}
/* Compute the diurnal arc that the Sun traverses to reach */
/* the specified altitude altit: */
do {
let cost: Double = ( sind(x: altit) - sind(x: lat) * sin_sdecl ) / ( cosd(x: lat) * cos_sdecl );
if cost >= 1.0 {
t = 0.0 /* Sun always below altit */
}
else if cost <= -1.0 {
t = 24.0; /* Sun always above altit */
}
else {
t = (2.0/15.0) * acosd(x: cost); /* The diurnal arc, hours */
}
}
return t;
} /* __daylen__ */
/// This function computes the Sun's position at any instant.
private class func sunpos(d: Double) -> (lon: Double, r: Double ) {
/******************************************************/
/* Computes the Sun's ecliptic longitude and distance */
/* at an instant given in d, number of days since */
/* 2000 Jan 0.0. The Sun's ecliptic latitude is not */
/* computed, since it's always very near 0. */
/******************************************************/
var M: Double /* Mean anomaly of the Sun */
var w: Double /* Mean longitude of perihelion */
/* Note: Sun's mean longitude = M + w */
var e: Double /* Eccentricity of Earth's orbit */
var E: Double /* Eccentric anomaly */
var x: Double
var y: Double /* x, y coordinates in orbit */
var v: Double /* True anomaly */
/* Compute mean elements */
M = revolution( x: 356.0470 + 0.9856002585 * d );
w = 282.9404 + 4.70935E-5 * d;
e = 0.016709 - 1.151E-9 * d;
/* Compute true longitude and radius vector */
E = M + e * RADEG * sind(x: M) * ( 1.0 + e * cosd(x: M) );
x = cosd(x: E) - e;
y = sqrt( 1.0 - e*e ) * sind(x: E);
let r = sqrt( x*x + y*y ); /* Solar distance */
v = atan2d( y: y, x: x ); /* True anomaly */
var lon = v + w /* True solar longitude */
if lon >= 360.0 {
lon -= 360.0 /* Make it 0..360 degrees */
}
return (lon, r)
}
private class func sun_RA_dec( d: Double ) -> (RA: Double, dec: Double, r: Double ) {
/******************************************************/
/* Computes the Sun's equatorial coordinates RA, Decl */
/* and also its distance, at an instant given in d, */
/* the number of days since 2000 Jan 0.0. */
/******************************************************/
var obl_ecl: Double
var x: Double
var y: Double
var z: Double
/* Compute Sun's ecliptical coordinates */
let (lon, r) = sunpos( d: d )
/* Compute ecliptic rectangular coordinates (z=0) */
x = r * cosd(x: lon)
y = r * sind(x: lon)
/* Compute obliquity of ecliptic (inclination of Earth's axis) */
obl_ecl = 23.4393 - 3.563E-7 * d
/* Convert to equatorial rectangular coordinates - x is unchanged */
z = y * sind(x: obl_ecl)
y = y * cosd(x: obl_ecl)
/* Convert to spherical coordinates */
let RA = atan2d( y: y, x: x )
let dec = atan2d( y: z, x: sqrt(x*x + y*y) )
return (RA, dec, r)
} /* sun_RA_dec */
private static let INV360: Double = ( 1.0 / 360.0 )
/*******************************************************************/
/** This function reduces any angle to within the first revolution */
/** by subtracting or adding even multiples of 360.0 until the */
/** result is >= 0.0 and < 360.0 */
/*******************************************************************/
private class func revolution( x: Double ) -> Double {
/*****************************************/
/* Reduce angle to within 0..360 degrees */
/*****************************************/
return( x - 360.0 * floor( x * INV360 ) );
} /* revolution */
private class func rev180(x: Double ) -> Double {
/*********************************************/
/* Reduce angle to within +180..+180 degrees */
/*********************************************/
return( x - 360.0 * floor( x * INV360 + 0.5 ) );
} /* revolution */
/********************************************************************/
/** This function computes GMST0, the Greenwich Mean Sidereal Time */
/** at 0h UT (i.e. the sidereal time at the Greenwhich meridian at */
/** 0h UT). GMST is then the sidereal time at Greenwich at any */
/** time of the day. I've generalized GMST0 as well, and define it */
/** as: GMST0 = GMST - UT -- this allows GMST0 to be computed at */
/** other times than 0h UT as well. While this sounds somewhat */
/** contradictory, it is very practical: instead of computing */
/** GMST like: */
/** */
/** GMST = (GMST0) + UT * (366.2422/365.2422) */
/** */
/** where (GMST0) is the GMST last time UT was 0 hours, one simply */
/** computes: */
/** */
/** GMST = GMST0 + UT */
/** */
/** where GMST0 is the GMST "at 0h UT" but at the current moment! */
/** Defined in this way, GMST0 will increase with about 4 min a */
/** day. It also happens that GMST0 (in degrees, 1 hr = 15 degr) */
/** is equal to the Sun's mean longitude plus/minus 180 degrees! */
/** (if we neglect aberration, which amounts to 20 seconds of arc */
/** or 1.33 seconds of time) */
/** */
/********************************************************************/
private class func GMST0( d: Double ) -> Double {
var sidtim0: Double
/* Sidtime at 0h UT = L (Sun's mean longitude) + 180.0 degr */
/* L = M + w, as defined in sunpos(). Since I'm too lazy to */
/* add these numbers, I'll let the C compiler do it for me. */
/* Any decent C compiler will add the constants at compile */
/* time, imposing no runtime or code overhead. */
sidtim0 = revolution( x: ( 180.0 + 356.0470 + 282.9404 ) +
( 0.9856002585 + 4.70935E-5 ) * d )
return sidtim0
} /* GMST0 */
}